Services

Both alcohol use and anxiety are very common issues in modern society, and the relationship between the two is complicated and worth exploring.
Alcohol is the most commonly consumed and misused substance in the United States. In fact, the Delaware Behavioral Risk Factor Survey found that almost 57% of Delaware’s adult population reported drinking alcohol at least once in the last 30 days. They also found that the percentage of the adult population that regularly consumes at least some form of alcoholic beverages has remained largely unchanged in the last decade.
If a person finds alcohol has started to affect important aspects of their life, such as their career, relationships, or health, they may meet the criteria for alcohol use disorder (AUD).
When it comes to mental health issues, anxiety is a category that covers a wide range of common conditions, such as social anxiety disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and avoidant personality disorder.
It’s important to understand both of these issues individually to better understand how they relate to each other.
To a certain degree, anxiety is normal and a part of everyday life. Anxiety is your body’s natural response to stress and is marked by a feeling of fear or concern about what’s to come. Having worried and anxious feelings from time to time is a completely normal and healthy part of the human experience. Stressful situations present themselves on a regular basis as part of modern life, and anxiety can even help us perform at our most focused and alert.
Some examples of typical stress-causing situations may include public speaking, school exams, physical challenges such as sports, and job interviews.
For many people, anxiety can be an intrusive force that prevents them from enjoying day-to-day life in a healthy manner. When someone has extreme anxiety that affects important aspects of their life, they may be suffering from an anxiety disorder.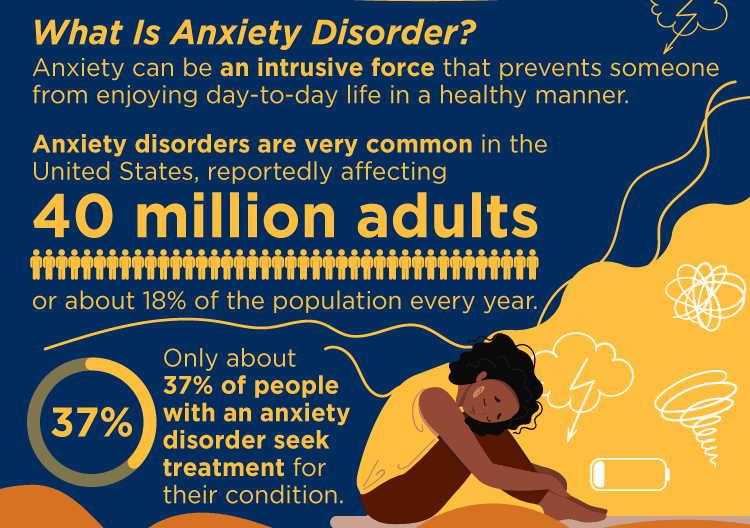
Anxiety disorders are very common in the United States, reportedly affecting 40 million adults or about 18% of the population every year. While anxiety disorders are highly treatable, only about 37% of people with an anxiety disorder seek treatment for their condition.
There are many different types of anxiety disorder, but to some extent, they all feature ongoing and excessive feelings of anxiety and worry that are difficult to control.
While there are many subsets that fall under the umbrella of anxiety disorder, some of the most common include:
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): GAD features constant, excessive, and unrealistic anxiety about various parts of life, including work, social relationships, financial matters, and others.
These feelings are often accompanied by physical symptoms such as dizziness, shortness of breath, and heart palpitations.
Social Anxiety Disorder: Also known as social phobia, social anxiety is a specific type of anxiety whose main feature is the fear of social situations. It’s a very broad disorder that can affect every aspect of a person’s life that involves interacting with other people.
People with social anxiety tend to be preoccupied with the potential of embarrassing themselves in public or doing something that will cause others to judge them.
Panic Disorder: Someone who suffers from panic disorder may have certain things or situations that trigger a physical response known as a panic attack. During a panic attack, the person may experience feelings of intense and irrational fear. They may also feel like they’ve lost all control of themselves.
Physical symptoms of a panic attack can be intense and include rapid heartbeat, chest or stomach pain, difficulty breathing, dizziness or weakness, sweating, hot and cold chills, or tingling and numbness in the hands.
Other Anxiety Disorders: Other serious, but less common, conditions that fall under the category of anxiety disorders include post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), avoidant personality disorder, and specific phobias or fears that can develop on their own or as the result of any other type of anxiety disorder.
Alcohol is what is known as a central nervous system depressant, and in the beginning, it has a calming and relaxing effect on the user. These desired effects of alcohol use are actually the result of the drug interfering with the way the brain naturally communicates.
Alcohol also affects the pleasure centers of the brain, telling them to create a neurotransmitter (signal carrier) called dopamine. Dopamine is the chemical messenger that’s responsible for many feelings of happiness, contentment, pleasure, and even memory. The more habitual the alcohol use becomes, the more the brain gets used to having this new source of dopamine.
When the drinking is suddenly stopped, the brain’s natural systems keep trying to function abnormally because that’s what the alcohol taught them to do. This leads to a lack of dopamine and other effects that cause negative issues related to alcohol withdrawal.
Anxiety is a disorder that mostly affects the central nervous system, or CNS. It can tell your body to increase its heart rate, increase blood flow, and push your brain into panic mode. In many cases of anxiety disorder, medication is necessary, and doctors will typically prescribe anti-anxiety medications known as benzodiazepines.
Like alcohol, benzodiazepines are also CNS depressants. Because of this similarity, many people at first find that alcohol may help them relax by suppressing some of the symptoms of their anxiety.
As mentioned above, over 60% of people who suffer from an anxiety disorder do not seek professional treatment. Along with this, the Anxiety and Depression Association of America has found that about 20% of people who suffer from social anxiety disorder also suffer from alcohol use disorder or alcohol dependence. When a person suffers from both a mental health disorder as well as a substance use disorder, they have what is known as co-occurring disorders. Co-occurring disorders treatment requires a special approach from experienced and compassionate mental health professionals.
Some of these people may consume alcohol in an effort to self-medicate. Self-medication is when a person uses substances, such as alcohol, without the guidance of a medical professional in an attempt to find relief from emotional or physical pain.
While they may find the alcohol can provide anxiety relief at first, that slight amount of relief can come at a great cost as they risk alcohol dependence and serious impacts on their health.
Yes, alcohol can both cause and worsen anxiety.
Short-term Effects:
The short-term worsening of anxiety typically occurs when the alcohol’s effects wear off in what’s commonly known as a hangover. During a hangover, a person can expect to feel many physical symptoms that stem from lack of sleep, muscle fatigue, and dehydration. The person will also feel some mental and emotional symptoms, including depression and anxiety.
This has to do with how alcohol interacts with the brain, as mentioned above. Alcohol use tells the brain to release dopamine, serotonin, and other chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters are responsible for positive emotions like pleasure and contentment.
In a brain that functions normally, these chemicals are released when you do something that inspires joy or pleasure, such as working out or accomplishing a goal. When a person drinks alcohol, it tells the brain to release these chemicals all at once. This means it will provide temporary relief and relaxation. Once alcohol has left the body, the person will typically feel depression, anxiety, and other negative emotions as the brain takes time to recover and return to normal function.
Alcohol-induced anxiety can last anywhere from a few hours after alcohol leaves the system all the way up to a couple of days.
Long-term Effects:
The long-term, heavy consumption of alcohol can have very serious effects on the body and brain. The health risks of long-term, chronic alcohol use include heart, liver, and digestive problems, cancer, weakening of the immune system, mood and sleep disturbances, and the development of mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
Although alcohol can provide temporary relief for some kinds of anxiety, alcohol use can be a slippery slope that ends in physical dependence. Eventually, the negative effects of drinking make themselves known in various ways, including an increase in anxiety and depression. Everyone’s body processes alcohol differently, so there is no one answer for how much drinking is too much.
That said, alcohol use disorder (AUD) as a medical diagnosis has a certain set of criteria that may suggest someone has a problem with drinking. There are a number of certain behavioral patterns to look out for when determining if you or a loved one is suffering from AUD.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) states that anyone who meets 2 of the 11 following criteria within a 12-month period may be diagnosed with an AUD. Here are some questions to consider to accurately assess whether you or a loved one may be suffering from a problem with alcohol.
In the past year, have you:
If any of these symptoms are things you or a loved one has experienced, your drinking habits may already be cause for concern. The more symptoms you’ve had, the more likely it is you’ve become physically dependent on alcohol.
There are many treatment options for anxiety that are effective in addressing anxiety issues.
Treatments may depend on the type of anxiety you’re experiencing.
If you’re suffering from generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), or an ongoing feeling of stress or worry without a specific cause, your doctor may suggest learning different skills and behaviors that may help you stop avoiding activities due to anxiety. This is a strategy called cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and is found to be effective in treating many mental health issues.
Medications can also be an effective tool in treating anxiety.
Different types of medication can treat anxiety in different ways. Antidepressants may be taken daily to help reduce anxiety overall. Anti-anxiety medications (benzodiazepines) are generally used for temporary relief from intrusive feelings of anxiety. Many people find success in treating their social anxiety with a combination of therapy and medication such as sertraline (Zoloft). You and your doctor will work together to determine which approach may be best for you and your situation.
While drinking alcohol can have negative effects on its own, it’s very important to know how alcohol can interact with any other medications you are taking. When medications such as benzodiazepines are taken along with alcohol, the effects can be fatal. Both drugs are central nervous system (CNS) depressants, and using them together can slow down essential body functions, such as breathing and heart rate, to a halt.
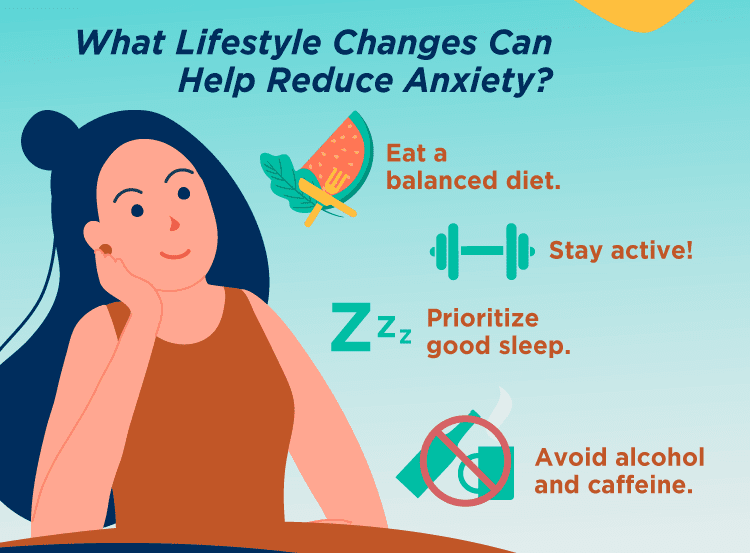
While anxiety can be treated, it is not always curable. However, there are certain lifestyle changes and strategies that can help you reduce anxiety and learn to cope with it. Some of these lifestyle changes can include:
There are some coping strategies that help by curbing anxiety before it can develop into intense anxiety or panic attacks. Some of those strategies include:
SUN Behavioral Delaware will teach you strength-based strategies to equip you to neutralize anxious thoughts without the use of alcohol or other harmful substances. Our program provides these treatments in a trauma-informed-care environment with the core principles of safety, trustworthiness, empowerment, collaboration, and choice driving all interactions.
There are many outpatient treatment options available for managing anxiety disorders, but cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) has been shown to be the most effective way to help people overcome their anxiety.
Cognitive behavioral therapy changes thoughts, feelings, core beliefs, and actions that drive the issues you’re facing. It goes far beyond medication to help you identify the negative thoughts contributing to anxiety and your responses in situations that can further your anxiety.
Call us today at 302-604-5600 to start getting your life back from the clutches of anxiety and alcohol use.
Alcohol does not help anxiety and can even make it worse. Because alcohol is a depressant, a person may feel down or sluggish when drinking alcohol, a feeling -- both emotionally and physically -- that can get worse when the alcohol leaves someone’s system. If someone who is already struggling with anxiety decides to drink regularly, they may be making their anxiety worse by letting it go untreated, but also through the back and forth stress of drinking, sobering up, and drinking again.
It can make them worse. Anxiety and panic attacks do not typically develop due to someone drinking alcohol, though each person is different. Alcohol can increase feelings of anxiousness or panic when someone sobers up and their body begins to feel the effects of heavy drinking.
It can differ drastically from person to person, but anxiety may feel like you cannot catch your breath; like you are jittery or unable to sit still; like your brain is on a constant loop of thoughts, worries, and emotions. Anxiety, in general, can be described as feeling “on edge,” unable to achieve a relaxing and calm mindset.
There are many options, but one of the most important is to consider your drinking and confront whether you have a problem. Consulting your doctor is another good way to figure out if your anxiety is generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) or triggered by something else. You can also meditate, write about your thoughts and emotions in a journal, or go for a leisurely walk (or exercise in some other way)